West Nile Virus Found In Wichita Falls
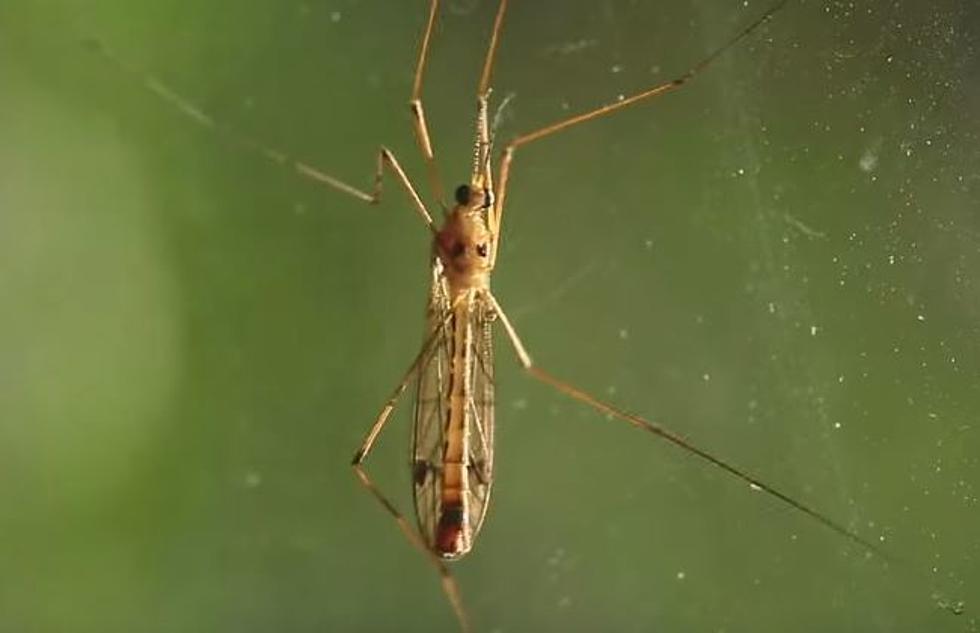
It's here again. The Wichita county Public Health Department is saying they have their first case this year of West Nile in Wichita Falls.
The person infected already has a compromised immune system and that is really dangerous. But, where there is one mosquito with West Nile, there are more and that puts you and your family at risk.
Protect Yourself With These Easy Tips
- Wear long sleeves and pants when you're outside at dusk and dawn.
- Wear bug spray with DEET when you're outside at dusk and dawn. Spray it over your clothes, too.
- Don't let water stand around your yard.
What will West Nile really do to you? Fortunately, most people infected with WNV will have no symptoms. About 1 in 5 people who are infected will develop a fever with other symptoms. Less than 1% of infected people develop a serious, sometimes fatal, neurological illness. To give you even more info, we've contacted the Centers for Disease Control and gotten these great answers to their frequently asked questions:
What is West Nile virus?
West Nile virus is most commonly spread by infected mosquitoes. West Nile virus can cause illness, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) or meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain and spinal cord). It was first detected in North America in 1999, and has since spread across the continental United States and Canada.
How do people get infected with West Nile virus?
Most people get infected with West Nile virus by the bite of an infected mosquito. Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on infected birds. Infected mosquitoes can then spread the virus to humans and other animals. In a very small number of cases, West Nile virus has been spread through blood transfusions, organ transplants, and from mother to baby during pregnancy, delivery, or breastfeeding.
Who is at risk for infection with West Nile virus?
Anyone living in an area where West Nile virus is present in mosquitoes can get infected. West Nile virus has been detected in all lower 48 states (not in Hawaii or Alaska). Outbreaks have been occurring every summer since 1999. The risk of infection is highest for people who work outside or participate in outdoor activities because of greater exposure to mosquitoes.
Is there a vaccine available to protect people from West Nile virus?
No. Currently there is no West Nile virus vaccine available for people. Many scientists are working on this issue, and there is hope that a vaccine will become available in the future.
How soon do people get sick after getting bitten by an infected mosquito?
The incubation period is usually 2 to 6 days but ranges from 2 to 14 days. This period can be longer in people with certain medical conditions that affect the immune system.
What are the symptoms of West Nile virus disease?
Most people (70-80%) who become infected with West Nile virus do not develop any symptoms. About 1 in 5 people who are infected will develop a fever with other symptoms such as headache, body aches, joint pains, vomiting, diarrhea, or rash. Most people with this type of West Nile virus disease recover completely, but fatigue and weakness can last for weeks or months. Less than 1% of people who are infected will develop a serious neurological illness such as encephalitis or meningitis (inflammation of the brain or surrounding tissues). The symptoms of neurological illness can include headache, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, coma, tremors, seizures, or paralysis. Some of the neurological effects may be permanent. About 10 percent of people who develop neurological infection due to West Nile virus will die.
Who is at risk for serious illness if infected with West Nile virus?
Serious illness can occur in people of any age. However, people over 60 years of age are at the greatest risk for severe disease. People with certain medical conditions, such as cancer, diabetes, hypertension, kidney disease, and people who have received organ transplants, are also at greater risk for serious illness.
How is West Nile virus disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis is based on a combination of clinical signs and symptoms and specialized laboratory tests of blood or spinal fluid. These tests typically detect antibodies that the immune system makes against the viral infection.
What is the treatment for West Nile virus disease?
There are no medications to treat or vaccines to prevent West Nile virus infection. Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used to reduce fever and relieve some symptoms. People with milder symptoms typically recover on their own, although some symptoms may last for several weeks. In more severe cases, patients often need to be hospitalized to receive supportive treatment, such as intravenous fluids, pain medication, and nursing care.
When do most cases of West Nile virus disease occur?
Most people are infected from June through September.
Why do my state health department and CDC sometimes report different numbers of West Nile virus cases?
The CDC case count is based on the number of cases that have been reported by each state health department to CDC. The CDC case count is updated once a week during the transmission season. State health departments might update their counts more often.
More From KZCD-FM